論文情報
著者:Hasegawa, T., Fujimori, S., Ito, A., Takahashi, K., Masui, T.
発表年:2016
雑誌名:Science of Total Environment
論文へのリンク(英文のみ)
キーワード
Land-use change, Spatial allocation, Integrated assessment
概要
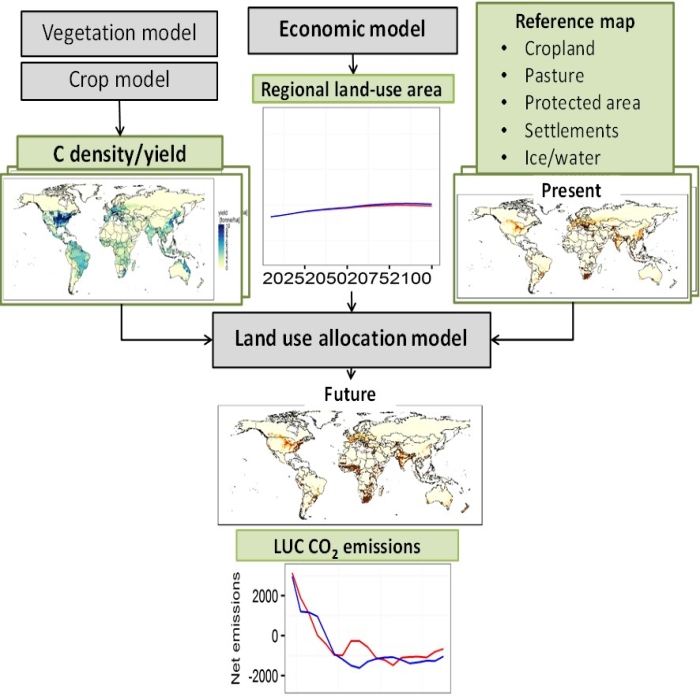
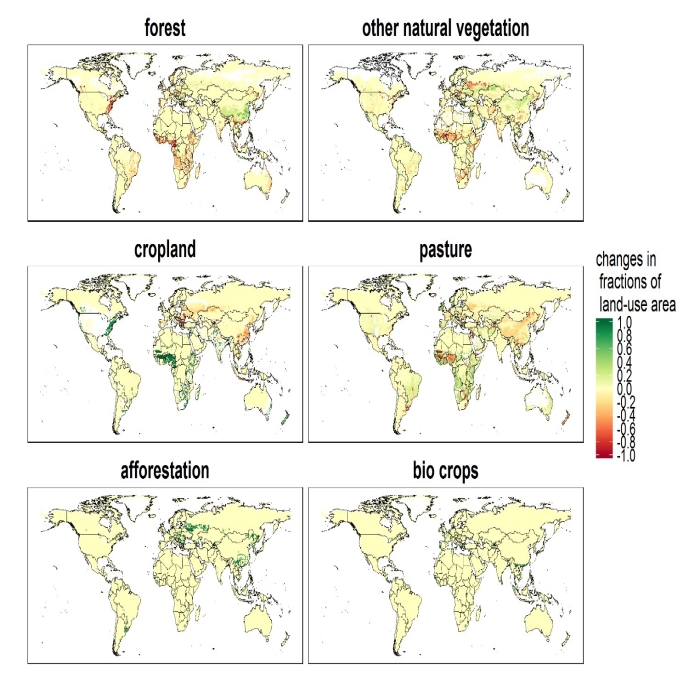
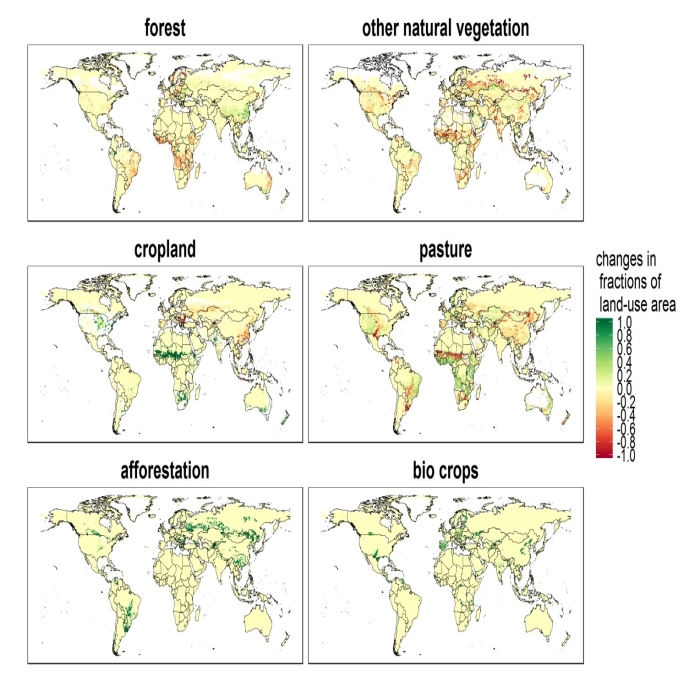
We developed a global land-use allocation model that can be linked to integrated assessment models (IAMs) with a coarser spatial resolution. Using the model, we performed a downscaling of the IAMs’ regional aggregated land-use projections to obtain a spatial land-use distribution, which could subsequently be used by Earth system models for global environmental assessments of ecosystem services, food security, and climate policies. Here we describe the land-use allocation model, discuss the verification of the downscaling technique, and explain the influences of the downscaling on estimates of land-use carbon emissions. A comparison of the emissions estimated with and without downscaling suggested that the land-use downscaling would help capture the spatial distribution of carbon stock density and regional heterogeneity of carbon emissions caused by cropland and pasture land expansion.
本研究は、世界を集約的な17地域で表した統合評価モデル(IAM)にリンクできるグローバルな土地利用配分モデルを開発しました。そして、IAMsの地域集約土地利用予測から地球システムモデルが生態系サービス、食糧安全保障、気候政策の地球環境評価に使用できるような詳細な空間的土地利用分布を得ました。 本論文では、土地利用配分モデルについて説明し、ダウンスケール手法の検証を行い、それが土地利用炭素排出量の推計に及ぼす影響を議論します。ダウンスケーリングを実施した場合とそうでない場合の二酸化炭素排出量を比較すると、土地利用のダウンスケーリングは、農地と牧草地の拡大による炭素ストック密度の空間的分布と炭素排出の地域的異質性を適切に反映できることが示唆されました。