論文情報
著者: Lu Gao, Yuki Hiruta, Shuichi Ashina
年:2020
掲載誌:Renewable Energy, Volume 162, Pages 818-830
論文へのリンク(英文のみ)
キーワード
Willingness to pay, Renewables, Investment subsidy, Low-carbon society
要旨
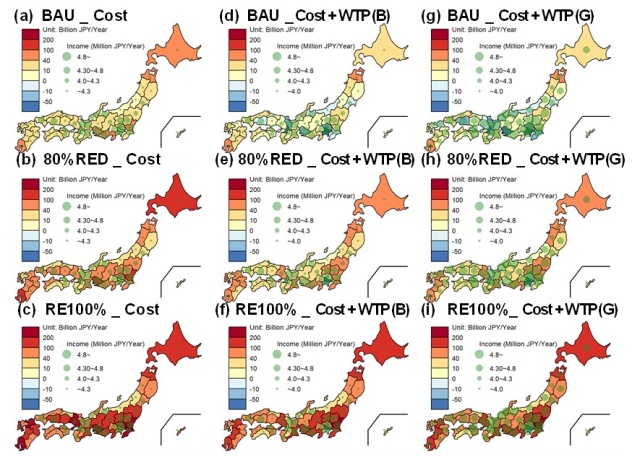
This study aims to assess the impact of willingness to pay (WTP) on achieving future renewable energy (RE) resource targets in Japan. Electricity production from RE is an effective measure to mitigate climate change. As a policy to promote renewable electricity technologies deployment, the cost of RE is generally covered by a levy, which usually ignore user’s attitudes or affordability, and may become increasingly dissatisfied by consumer for its increase with the RE expansion. Considering the potentially crucial role of WTP in levy decision for RE, we developed a series of models to simulate WTP through 2030 under three RE development scenarios and two economic growth cases. This allowed evaluation of the necessary investment subsidies for adopting RE to meet national targets in each prefecture of Japan. Median WTP is estimated to increase from approximately 1000 to 2400 JPY/(household·month) during 2015–2030. The investment required to meet future RE targets decreases sharply with increases in WTP by consumers. In particular, for prefectures with high WTP such as Tokyo, the investment required could be covered only by consumers’ WTP; no subsidies would be required. These results highlighted the opportunities of WTP assessment for efficient utilization of government subsidies for shifting towards greater use of renewable energy with flexible energy polices by policy-makers.