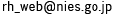PJ4 Environmental Fate Project
Modeling the environmental fate of the pollutome
We are developing and improving methods to derive emission inventories, physicochemical parameters, bioaccumulation properties, and multimedia models to evaluate the environmental fate of all substances of concern for which we have only limited risk evaluation information; these methods will contribute to exposure assessments. These methods include a novel emission estimation method, focusing on substances categorized into the same usage, and bioaccumulation models applicable to polar and ionic organic substances.
Related Information
HarmoNIES No.4
Reproducing the Environment to Uncover the Movement of Chemicals
-Tracking Chemicals with Computer Simulations-
Interview with a researcher who developing a multimedia environmental fate model and website (database) on environmental risk assessment of chemical substances.
Grid-Catchment Integrated Environmental Modeling System (G-CIEMS) (in Japanese)
(in Japanese)
Simulates the environmental fate of contaminants throughout Japan
G-CIEMS is a spatially resolved and geo-referenced, dynamic, multimedia environmental fate model. This model predicts the concentrations of chemicals in the atmosphere, surface waters, surface water sediments, surface soils, coastal waters, and sewage collection areas based on environmental emissions and physicochemical properties of the target substances and use of geographical and meteorological information.