Information of Paper
Author: Yamaguchi Rintaro
Year:2018
Journal:Environmental and Resource Economics, forth coming
Link to the paper
Keywords
Discounting; Income distribution; Intragenerational equity; Climate change
Abstract
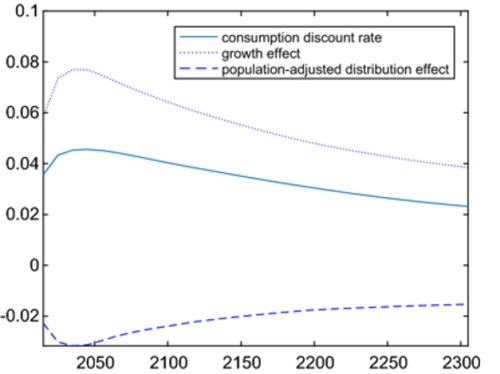
It is now established that the consumption discount rate is determined by the growth of consumption multiplied by the elasticity of marginal utility, but distributive concerns are rarely reflected in the literature. Assuming a social welfare function with inequality aversion, we consider a consumption discount rate that can be decomposed into the growth effect and the intragenerational distribution effect. The framework is then extended to include population change and inequality in the environment as an amenity in a utility with constant elasticity of substitution. Numerical examples illustrate that distributional effects turn non-negligibly negative, that may reduce consumption discount rate by 1–3% for plausible parameters, once distribution is adjusted for both population and the environment.