| Invasion information |
| Range in Japan |
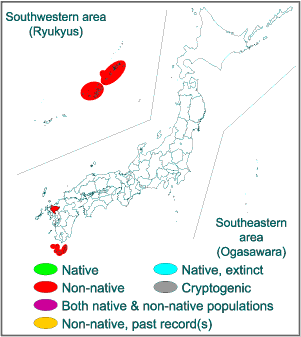
Chichijima (Ogasawara), Hachijojima (Izu Islands), Madarajima (Saga Pref.), a part of Goto Islands), Uji Islands, Yakushima (Osumi Islands), Akusekijima, Gajajima (Tokara Islands), Amamioshima, Tokunoshima (Amami Islands), Ihejima, Yanahajima, Agunijima, Kerama Islands (Okinawa islands), Iriomotejima, and Uotsurijima (Sakishima Islands). |
|
| Origin |
Unknown. Various strains have possibly been introduced repeatedly. |
| Date |
Introduced to Ryukyus in 15C, to mainland since late 19C. According to old literature, feral goat in Ogasawara was not observed in 1824 and already established in 1853. |
| Route |
Deliberate: Escape or release of domestic animals. |
| Impact |
Feeding on various plants and destruction of vegetation. This cause decline of endangered and endemic plants, destruction of bird habitat, incursion of soil to sea, which cause degradation of coral reef and fishery site. Damage on agriculture. Pollution by feces.
Native organism(s) affected: Various plants (e.g., Lobelia boninensis, Cirsium boninense, Crepidiastrum ameristophyllum, Asarum senkakuinsulare, Hypericum senkakuinsulare, and Limonium senkakuense), birds (e.g., Phoebastria nigripes, Sula leucogaster, Puffinus pacificus), Mogera uchidai, coral reef. Crops and fishery resources. |
| Regulation in Japan |
Controled by several local ordinances: In Saga Pref., moving and trade are prohibited; In Amami City of Kagoshima Pref. and Hachijojima Is. of Izu Islands, goat owners must register and keep their goats within fences. |
| Introduced range in other countries |
Various islands. Fiji, Bahamas, Haiti, Cayman Islands, Cook Islands, Dominican Republic, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, Reunion, Canary Islands, etc. |

 Japanese |
English
Japanese |
English