- Ecol Soc Jpn (ed) (2002) Handbook of Alien Species in Japan. Chijinshokan, Tokyo (in Jpn)
- Ernst et al. (1989) Turtles of the World. Smithonian Institution Press.
- Environment Agency (2000) Threatened Wildlife of Japan Red Data Book 2nd ed. Reptilia/Amphibia. JWRC, Tokyo (in Jpn)
- Maenosono & Toda (2007) Distribution of amphibians and terrestrial reptiles in the Ryukyu Archipelago: A review of published records. Akamata. 18, 28-46 (in Jpn)
- Matsuo (2004) Amphibians and Reptiles of Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. Nagasaki Shinbunsha (in Jpn)
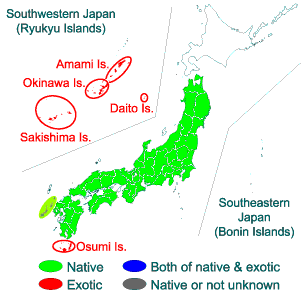
- Ota et al. (2004) Feral population of amphibians and reptiles in the Ryukyu Archipelago, Japan. Global Environmental Research. 8(2):133-143
- Sato & Ota (1999) False biogeographical pattern derived from artificial animal transportations: a case of the soft-shelled turtle, Pelodiscus sinensis, in the Ryukyu Archipelago, Japan. pp.317-334. Ota (ed.) Tropical Island Herpetofauna: Origin, Current Diversity, and Conservation. Elsevier Science B. V., Amsterdam.
- Sengoku et al. (eds) (1996) The Encyclopedia of Animals in Japan 5 Amphibians, Reptiles, Chondrichthyes. Heibonsha, Tokyo (in Jpn)
- Uetz et al. (1995-2010) TIGR Reptile Database http://www.reptiliaweb.org/.
- Yasukawa (2005) Alien freshwater turtles which may become established in Japan in the near future. Bull Herpetol Soc Jpn. 2005(2), 155-163 (in Jpn)
|
The populations of mainland of Japan and Taiwan are sometimes classified to different subspecies, P. s. japonicus and P. s. sinensis respectively.
|

 Japanese |
English
Japanese |
English